Declarations of the 9th FOCAC summit on strengthening China-Africa cooperation

FOCAC 2024 ,
Thursday, 5 September, 2024
McCreadie Andias
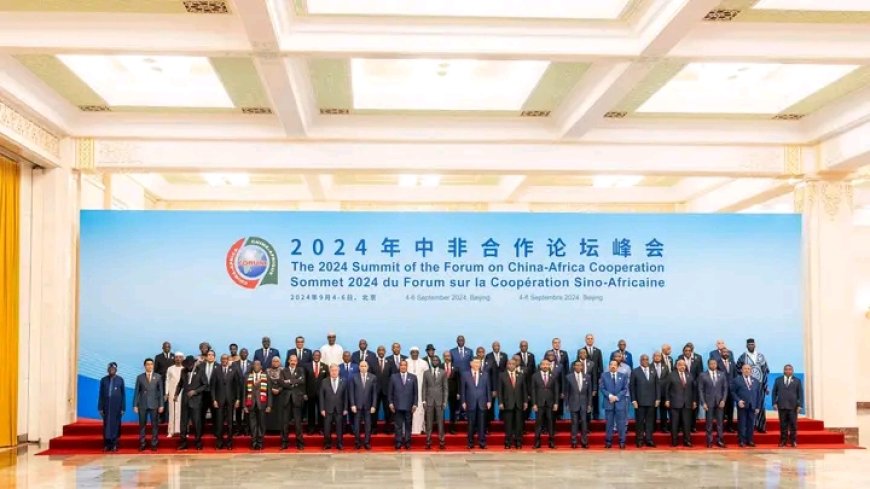
53 African Heads of State and Government, Delegations of the People’s Republic of China and the AU delegation convened in China from September 4 to 6 for the 2024 Beijing Summit of the Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC).
Under the theme “Joining Hands to Advance Modernization and Build a High-Level China-Africa Community with a Shared Future,” the Summit adopted by consensus the Beijing Declaration on Jointly Building an All-Weather China-Africa Community with a Shared Future for the New Era.
What is the FOCAC?
The Forum on China-Africa Cooperation was established in 2000 to formalise the strategic partnership between China and African nations. A summit is conducted every three years, with the host alternating between China and an African member
Declarations of the 9th FOCAC
During the 9th FOCAC summit. President Xi Jinping of China announced a 10-point partnership action plan for Africa for the next three years.
These include the modernisation of industrialisation, agriculture, trade, investment, training, and infrastructure.
Others are access for Africa’s goods to the Chinese market, 30 infrastructure connectivity projects and development cooperation comprising 1,000 livelihood projects.
President Xi Jinping pledged $51 billion of funding to African countries to support 30 infrastructure projects across the continent, with 360 billion yuan ($50.7 billion) to be offered as financial assistance.
“China is prepared to implement 30 infrastructure connectivity projects in Africa, promote high-quality Belt and Road cooperation and put in place a China-Africa network featuring land-sea links and coordinated development,”President Xi said.
“In the next three years, China will work with Africa to take 10 partnership actions for modernisation to deepen China-Africa cooperation and spearhead Global South modernisation,” he said.
He said it will include a $29.4 billion credit line, $11.2 billion of various forms of assistance and at least $9.8 billion of investment in Africa by Chinese companies.
China reaffirmed its firm support for Africa’s efforts to safeguard national independence and unity, territorial integrity, sovereignty, security and development interests.
Africa in return reaffirmed its firm commitment to the one-China principle, and reaffirms that there is but one China in the world, Taiwan is an inalienable part of China’s territory and the Government of the People’s Republic of China is the sole legal government representing the whole of China, and firmly supports all efforts by the Chinese government to achieve national reunification.
China recognized that promoting and protecting human rights including the right to development is a common cause of all humanity. It firmly opposed politicization of human rights agenda and politicization of the United Nations Human Rights Council and its relevant mechanisms, and opposed all forms of neocolonialism and international economic exploitation.
It called on the international community to resolutely resist and combat all forms of racism and racial discrimination, and oppose acts of intolerance, stigmatization, and incitement to violence against people based on religion or belief.
China and Africa jointly called for an equal and orderly multipolar world, and firmly safeguard the international system with the U.N. Here the leaders called for necessary reform and strengthening of the U.N. including its Security Council, redressing the historical injustices done to Africa, and increasing the representation of developing countries, African countries in particular, in the U.N. and its Security Council. China also vowed to support making special arrangements on the U.N. Security Council reform to meet Africa’s aspiration as a priority.
China supported Africa’s call for a universally beneficial and inclusive economic globalization that meets the common needs of all countries, especially the developing countries, and attach great importance to the concerns of African countries.
This is with respect to reforming the international financial system and improving development financing for countries in the Global South to realize common prosperity and better meet the development needs of African countries.
China committed to take an active part in and promote the reform of multilateral financial institutions, including quota, special drawing rights and voting rights reform of the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) while calling for increased representation for developing countries, so that the international monetary and financial systems will better reflect the changes in the international economic landscape in a more just way.
The summit highlighted the significance of the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) and recognized that the full implementation of the AfCFTA agreement will boost Africa’s economic development including through value addition and job creation.
China vowed to support Africa in strengthening trade integration, and will give continued support to the development of the AfCFTA and the application of Pan-African Payment and Settlement System. China will continue to support African countries in promoting African products through such platforms including the China International Import Expo and China-Africa Economic and Trade Expo.
China committed to support localized production and processing in Africa to help African countries achieve self-generated sustainable development by signing and implementing bilateral investment promotion and facilitation agreements with African countries, so as to provide a stable, fair and enabling business environment for Chinese and African businesses, and safeguard the safety, security and legitimate rights and interests of personnel, projects and institutions of the two sides.
Through investment, China will also support the development of African SMEs and encourages Africa to make good use of the Special Loan for the Development of African SMEs. The two sides commend the Alliance of Chinese business in Africa for Social Responsibilities (ACBASR) for implementing the initiative of “100 companies in 1,000 villages,” and guiding Chinese businesses in Africa to fulfill their social responsibilities.
China committed to support the role of the China-Africa Environmental Cooperation Center, the China-Africa Marine Science and Blue Economy Cooperation Center and the China-Africa Geosciences Cooperation Center in promoting the implementation of projects such as the China-Africa Green Envoys Program, the China-Africa Green Innovation Program and the Africa Solar Belt Program to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change.
On technological revolution and industrial transformation, China will work with Africa to accelerate the development of new quality productive forces, jointly boost innovation and market application of scientific and technological advances, and push forward full integration of digital and real economies.
The two agreed to join hands to halt abuses of AI through adoption of measures including the establishment of national code of conduct and expansion of digital literacy.
On peace and security im Africa. China vowed it's continued supports for U.N. funding for Africa’s independent peace operations pursuant to U.N. Security Council Resolution 2719.
China commended Africa’s efforts to combat the growing scourge of terrorism in Africa, particularly in the Horn of Africa and the Sahel, and called for the channeling of more global counterterrorism resources to developing countries to help African countries, particularly those affected, enhance their counterterrorism capacity building.
Furthermore the summit reaffirmed it's commitment to tackle emerging maritime security challenges facing African states, and combat transnational organized crimes such as drugs, weapons and human trafficking.
China applauded Africa for accelerating regional integration and its economic development through implementing the First Ten Year Implementation Plan of Agenda 2063 and launching the Second Ten Year Implementation Plan.
China expressed gratitude to Bassirou Diomaye Faye of the Republic of Senegal for co-chairing the 2024 Beijing Summit of FOCAC while it welcomed the Republic of the Congo as the co-chair of FOCAC from 2024 to 2027 and the Republic of Equatorial Guinea as the co-chair from 2027 to 2030.
The 10th FOCAC Ministerial Conference will be held in the Republic of the Congo in 2027.
What's Your Reaction?